![]()
Babies born on the first day of 2025 aren’t just the first of the year-they are the first of a generation.
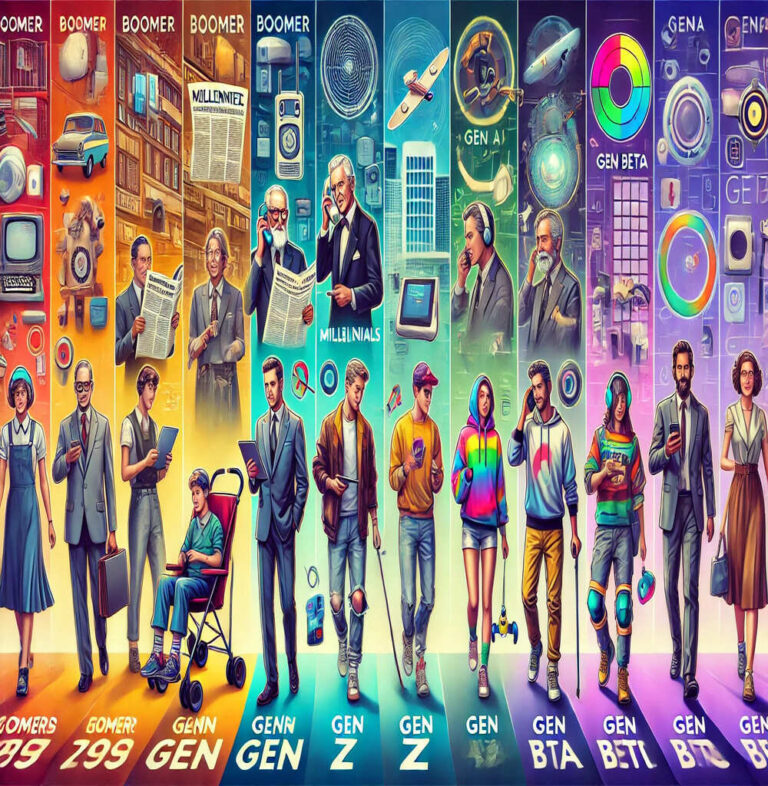
The incoming generation BETA – people born between 2025 and 2039 – is the seventh concurrent generation of our time.
They’re expected to make up 16% of global population and many of them are expected to live long enough to see the dawn of 22nd century.
“Each generation is characterized by its unique set of values, beliefs, and experiences, which often lead to a desire to surpass and influence the next generation. This inherent dynamic can create conflict within families and society at large, fueling a perpetual debate over which generation is superior. As a result, a cycle of one-upmanship ensues, with each generation striving to assert its dominance and prove its worth over others.”

The “generation gap” refers to the differences in values, attitudes, and behaviors between people of different age groups, typically between parents and children or grandparents and grandchildren. Each generation often believes their values and ways were better than the current generation’s. This leads to misunderstandings, conflicts, and a sense of disconnection between generations. Ultimately, it’s a natural phenomenon, but one that can be bridged with empathy and understanding.
Generations Overview – Merits and Demerits of each Generation (1900-2024)
Generational studies categorize people born within specific timeframes, shaped by historical, technological, and societal changes. Below is a detailed discussion of the characteristics, advantages, disadvantages, and impacts of each generation.
1. The Greatest Generation (1901–1927)
Characteristics:
Lived through World Wars, the Great Depression, and significant technological advancements like the automobile and radio.
Advantages:
- Strong sense of duty, resilience, and community spirit.
- Built foundational industries and infrastructure.
- Advocated for societal unity.
Disadvantages:
- Limited access to education for many.
- Traditional views, sometimes resistant to cultural changes.
Impact:
- Economically, they laid the groundwork for post-WWII industrial growth.
- Socially, they promoted collective responsibility.
- Culturally, they valued patriotism and hard work.
2. Silent Generation (1928–1945)
Characteristics:
Grew up during WWII and the early Cold War; known for discipline and loyalty.
Advantages:
- Benefited from post-WWII economic boom.
- Valued stability and conformity, which bolstered institutional growth.
Disadvantages:
- Hesitant to challenge authority, leading to slower social reforms.
- Lived in a highly patriarchal society.
Impact:
- Economically contributed to the rise of the middle class.
- Culturally, fostered early civil rights movements and technological innovation.
3. Baby Boomers (1946–1964)
Characteristics:
Born in an era of prosperity post-WWII; witnessed the Cold War, civil rights movements, and technological breakthroughs like television.
Advantages:
- Access to quality education and stable employment.
- Drivers of consumerism and suburbanization.
Disadvantages:
- Criticized for environmental degradation and excessive resource consumption.
- Economic policies favored them, leaving younger generations with challenges.
Impact:
- Socially, they pushed for equality and rights.
- Economically, they created wealth but also inequality.
- Culturally, they promoted individualism.
4. Generation X (1965–1980)
Characteristics:
Grew up during the rise of personal computing and globalization; the “latchkey” generation.
Advantages:
- Adaptability to changing technologies and work environments.
- Independent and entrepreneurial.
Disadvantages:
- Struggled with job security due to economic recessions.
- Experienced cultural fragmentation.
Impact:
- Socially bridged traditional and modern values.
- Economically, supported the rise of startups and tech industries.
- Culturally, introduced alternative music and subcultures.
5. Millennials (1981–1996)
Characteristics:
Shaped by the internet, 9/11, and social media. Tech-savvy and diverse.
Advantages:
- Highly educated and globally connected.
- Advocates for social justice and sustainability.
Disadvantages:
- Burdened by student debt and economic instability.
- Criticized for perceived entitlement.
Impact:
- Socially, they prioritized inclusivity and equality.
- Economically, drove the gig economy.
- Culturally, revolutionized media consumption.
6. Generation Z (1997–2012)
Characteristics:
Digital natives; grew up with smartphones and social media.
Advantages:
- Innovative and adaptive.
- Values mental health and activism.
Disadvantages:
- Short attention spans.
- Over-reliance on technology.
Impact:
- Socially, redefined activism through digital platforms.
- Economically, reshaped consumer behaviors toward digital services.
- Culturally, fostered new creative industries.
7. Generation Alpha (2013–2024)
Characteristics:
The first fully digital generation; raised in an AI-driven world.
Advantages:
- Unprecedented access to information.
- Early exposure to education and technology.
Disadvantages:
- Risk of digital addiction and reduced interpersonal skills.
- Overwhelmed by data and choices.
Impact:
- Socially, they will redefine relationships through AI.
- Economically, will lead in automation-driven industries.
- Culturally, expected to innovate new forms of art and media.
8. Generation Beta (2025–2039)
Characteristics:
Predicted to grow in a hyper-connected, climate-conscious, and AI-dominated world.
Potential Advantages:
- Mastery of advanced AI and biotech.
- Strong focus on sustainability and global collaboration.
Potential Disadvantages:
- Ethical challenges of AI and automation.
- Struggles with balancing technology and humanity.
Potential Impact:
- Socially, may redefine the concept of identity and relationships.
- Economically, will pioneer space exploration and green technologies.
- Culturally, expected to lead the fusion of human and AI creativity. Conclusion
Each generation reflects its era’s unique challenges and opportunities, contributing to societal evolution. The interplay of social, cultural, and economic factors ensures that every generation leaves a distinct mark, influencing the next. The coming Generation Beta will likely redefine human existence in profound ways.